Apr 05, 10 · Verify (1tan^2x)/(1cot^2x) = 1sec^2x Answered by a verified Math Tutor or Teacher We use cookies to give you the best possible experience on our website By continuing to use this site you consent to the use of cookies on your device as described in our cookie policy unless you have disabled themMath\int \frac{1\tan^2x}{1\tan^2x} \,dx/math math\int \frac{1\tan^2x}{\sec^2x} \,dx/math math\int \frac{1\tan^2x}{\frac{1}{\cos^2x}} \,dx/math math$$ \tan^2x \sec^2x $$ since $\sec ^2x=1\tan ^2 x$ so $$\tan^2x (1\tan ^2x)\implies 1$$ Share Cite Follow answered Jun 5 '13 at 1025 iostream007 iostream007 4,239 3 3 gold badges 19 19 silver badges 40 40 bronze badges $\endgroup$ Add a comment Your Answer
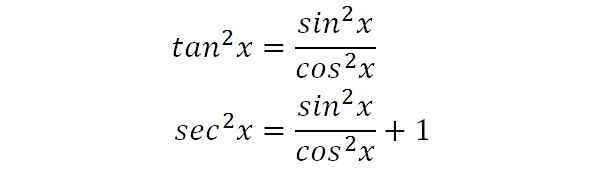
Integrate Sec 2x Method 2
5.25064634
5.25064634-This problem has been solved!Jan 08, 18 · Divide both side by cos^2x and we get sin^2x/cos^2x cos^2x/cos^2x = 1/cos^2x tan^2x 1 = sec^2x tan^2x = sec^2x 1 Confirming
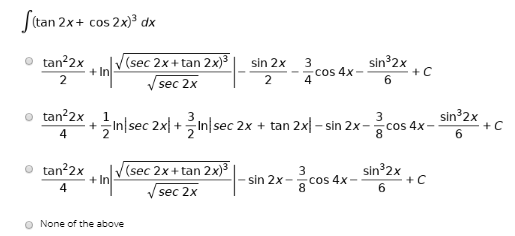


Answered Stan 2x Cos 2x Dx Tan 2x 2 V Sec 2x Bartleby
Adal2762 adal2762 05/29/19 Mathematics Middle School answered True or false the equation tan^2x1=sec^2x 1 See answer adal2762 is waiting for your help Add your answer and earn points kudzordzifrancis kudzordzifrancisLegend x and y are independent variables, ;Jul 29, 18 · The trigonometrical identity says 1tan^2x = sec^2 x that means sec^2 x tan^2 x = 1 However in our question, its tan^2 x sec^2 x or say sec^2 x tan^2 x = 1 which is completely against the identity Hense answer is False
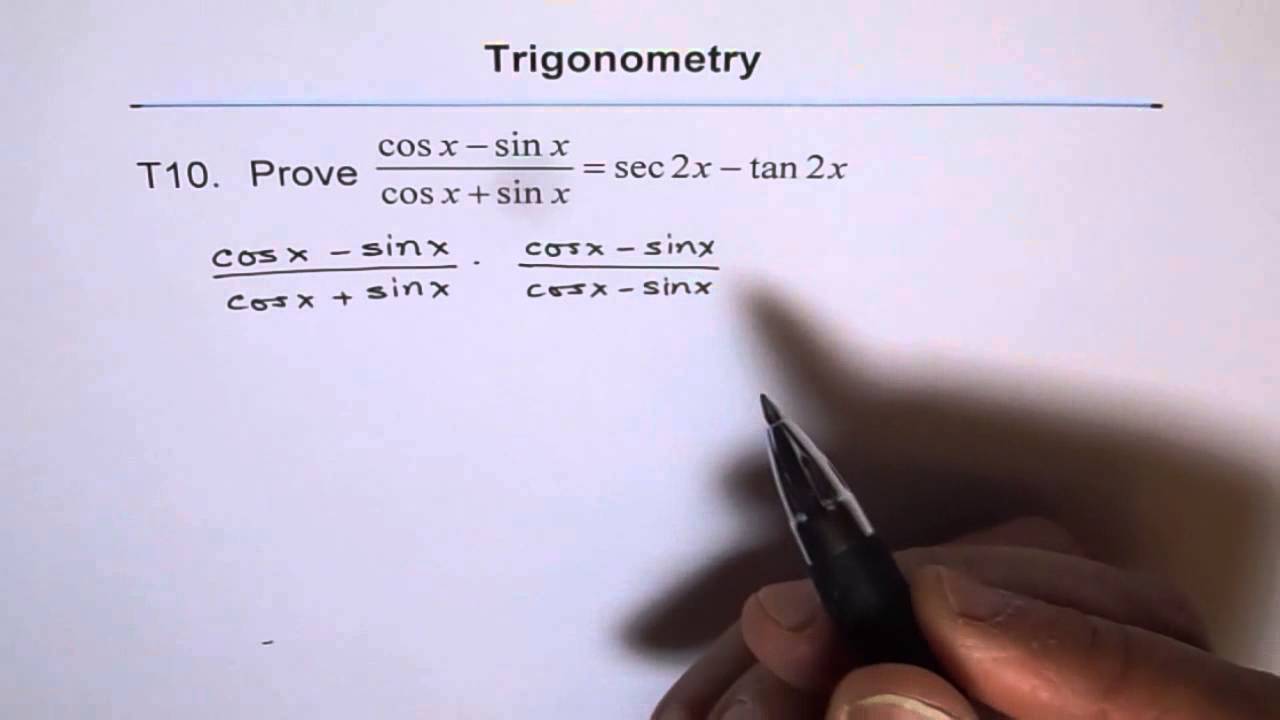
See the answer How do you solve this integral of 3 sec(2x1)tan(2x1)?Prove the identity ` ``(tan^2x)/(1tan^2x)=sin^2x ` Note that `tan^2x1=sec^2x=1/(cos^2x) ` and `tan^2x=(sin^2x)/(cos^2x) ` Substituting we get(sec^2x csc^2x)(tan^2x cot^2x) Found 2 solutions by ewatrrr, MathLover1 You can put this solution on YOUR website!
The derivative of a constant term is 0 The derivative of a x n is n a x n − 1 \sec (2x^ {1}1)\tan (2x^ {1}1)\times 2x^ {11} sec ( 2 x 1 − 1) tan ( 2 x 1 − 1) × 2 x 1 − 1 Simplify Simplify 2\sec (2x^ {1}1)\tan (2x^ {1}1) 2 sec ( 2 x 1 − 1) tan ( 2 x 1 − 1) For any term t, t^ {1}=tFree integral calculator solve indefinite, definite and multiple integrals with all the steps Type in any integral to get the solution, steps and graphMay 29, 19 · True or false the equation tan^2x1=sec^2x Get the answers you need, now!



Prove 1 Tan 2 Theta Sec 2 Theta Mathematics Stack Exchange



Sec 6x Tan 6x 1 3 Tan 2x Sec 2x Brainly In
D is the differential operator, int is the integration operator, C is the constant of integration Identities tan x = sin x/cos x equation 1 cot x = cos x/sin x equation 2 sec x = 1/cos x equation 3 csc x = 1/sin x equation 4The derivative of sec ( u 1) sec ( u 1) with respect to u 1 u 1 is sec ( u 1) tan ( u 1) sec ( u 1) tan ( u 1) Replace all occurrences of u 1 u 1 with 2 x 2 x Differentiate Tap for more steps Since 2 2 is constant with respect to x x, the derivative of 2 x 2 x with respect to x x is 2 d d x x 2 d d x xDec 21, · Functions involving trigonometric functions are useful as they are good at describing periodic behavior This section describes several techniques for finding antiderivatives of


Trig Identity Sec2x Minus Tan2x T10 Youtube



Differentiate The Following From First Principle Tan 2x 1
Tanx = t Sec^2 x dx= dt So now it is, 1/ (1t)^2 dt This integral is given by 1/1t and t= tanx So, it is cosx/cosx sinx tanx = t Sec^2 x dx= dt So now it is, 1/ (1t)^2 dt This integral is given by 1/1t and t= tanx So, it is cosx/cosx sinx Integral of the function \frac {\cos ^2 x} {1\tan x}Get an answer for 'solve tan^2xsecx =1 in the range 0°≤x≤ 360°' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotesFree trigonometric identities list trigonometric identities by request stepbystep



If Sec Tita X 1 4x Sec Tita Tan Tita 2x Or 1 2x Mathematics Topperlearning Com 15o2fj



Limit Trigonometric Function 2 Sec 2x 1 Tan X Youtube
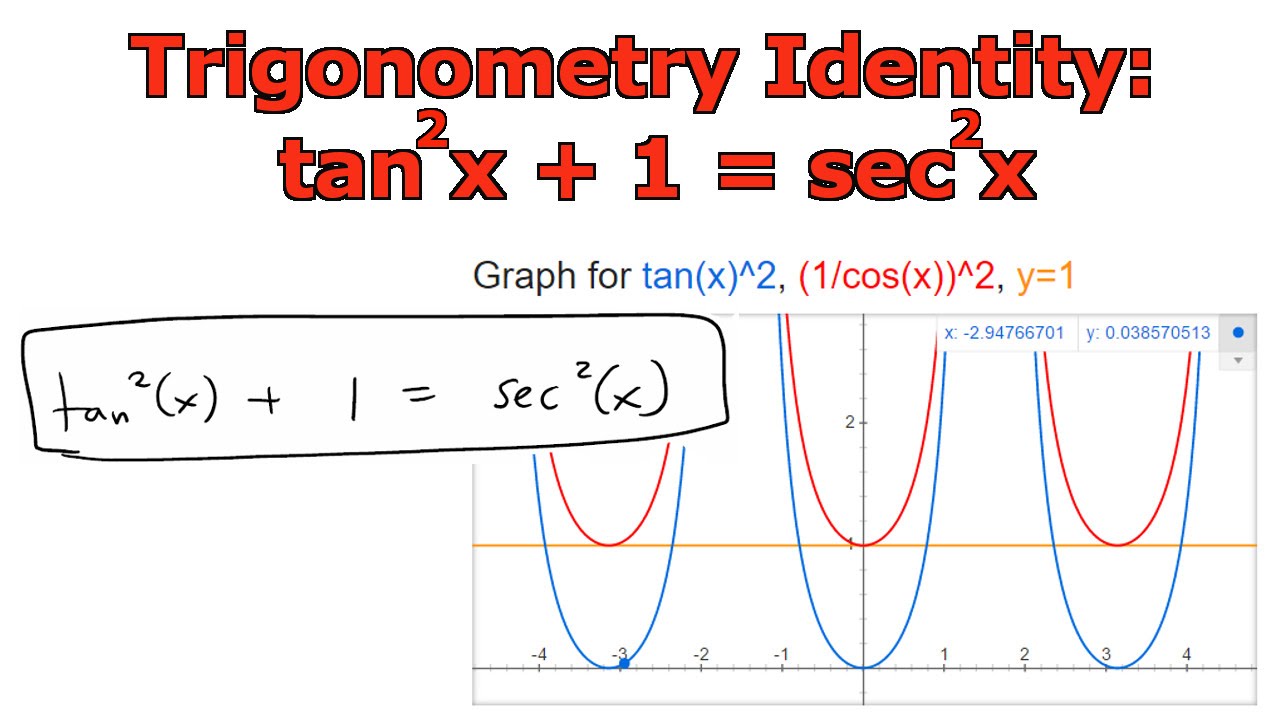
Tan^2xsec^2x/1tan^6x Ask questions, doubts, problems and we will help youQuestion How Do You Solve This Integral Of 3 Sec(2x1)tan(2x1)?Yes, sec 2 x−1=tan 2 x is an identity sec 2 −1=tan 2 x Let us derive the equation We know the identity sin 2 (x)cos 2 (x)=1 ——(i) Dividing throughout the equation by cos 2 (x) We get sin 2 (x)/cos 2 (x) cos 2 (x)/cos 2 (x) = 1/cos 2 (x) We know that sin 2 (x)/cos 2 (x)= tan 2 (x), and cos 2 (x)/cos 2 (x) = 1 So the equation (i) after substituting becomes



Consider The Following Equations 1 Cosec 2x Sec 2x Cosec 2xsec 2x 2 Sec 2x Tan 2x Sec 2xtan 2x 3 Cosec 2x Tan 2x Cot 2x


Trigonometric Substitution
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreSimplify and write the trigonometric expression in terms of sine and cosine (2tan^2x / sec^2x) 1 = (f (x))^2Calculus 2, integral of (1tan^2x)/sec^2x, integral of cos(2x)


Trigonometry Identity Tan 2 X 1 Sec 2 X Youtube



3 Sin Differentiate The Following Functions With Respect Tox 1 Sin 2x 4 Sin 1 Ax
Mar 13, 10 · Get an answer for 'verify (1 tan^2x)/(tan^2x) = csc^2x' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotesFree math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutorAn expansion of Pythagoras' Identity
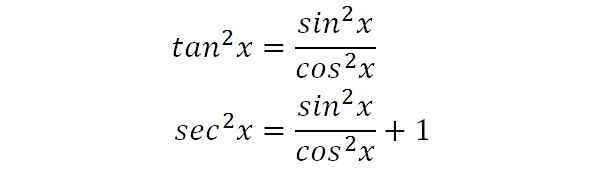


Integrate Sec 2x Method 2


Derivative Of Tan 2x Sec 2x
A follow up proof to accompany sin^2 cos^2 =1 Another identity that is used quite a bit, especially in calculus involving trigonometric functionsAug , · So, I figured out that $$\int\tan^2xdx =\int(\sec^2x1)dx=\tan xxC$$ I'm trying to adapt this so I can also evaluate $\int\tan^4x$ Stack Exchange Network Stack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build theirAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators



Cos2x Sin2x 1 1 Tan2x Sec2x Cot2x 1 Csc2x Cofunction
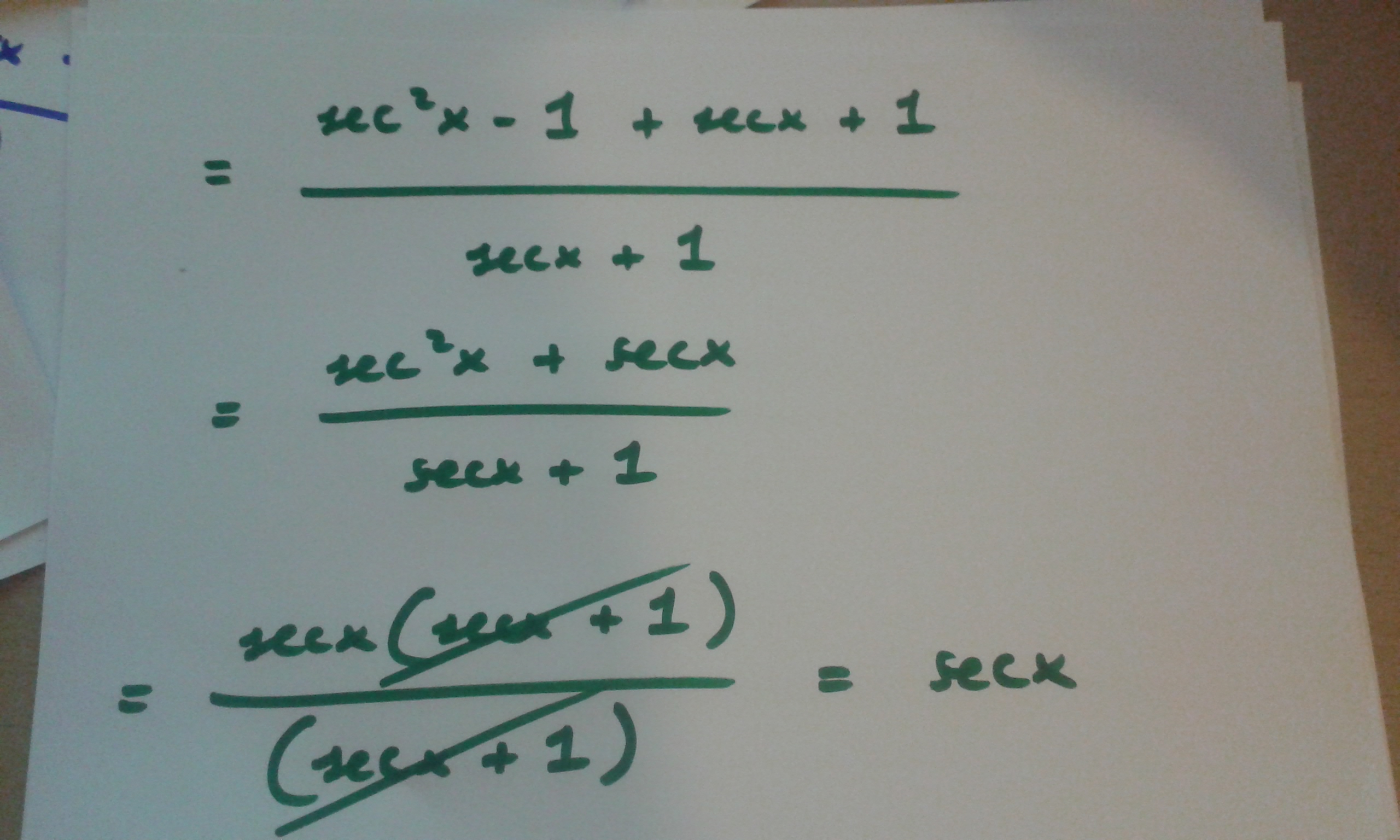


How Do You Prove Tan 2x Secx 1 1 Secx Socratic
\left(\sec(2x^{1})\right)^{2}\times 2x^{11} The derivative of a polynomial is the sum of the derivatives of its terms The derivative of a constant term is 0Feb 12, · Ex 34, 8 Find the general solution of the equation sec2 2x = 1 – tan 2x sec2 2x = 1 – tan 2x 1 tan2 2x = 1 – tan2x tan2 2x tan2x = 1 – 1 tan2 2x tan2x = 0 tan 2x (tan2x 1) = 0 Hence We know that sec2 x = 1 tan2 x So, sec2 2x = 1 tan2 2x tan 2x = 0 tan 2x 1 = 0 tan 2x = –1 We find general solutions for both separately General solution for tan 2x = 0 Let tan x = tan y tan 2x = tan 2y Also, tan 2x = 0 From (1) and (2) tan 2y = 0 We find solutions for tan 2x = 0 & tan 2xWe get (tan(x))2 1 = (sec(x))2 1 = (sec(x))2 (tan(x))2 Now, we will see if 1 = (sec(x))2 (tan(x))2and 1 = (sec(x))2 (tan(x))2 can both be true We can do this by assuming that they are both true, and then add the equations to get 2 = 2(sec(x))2 1=(sec(x))2
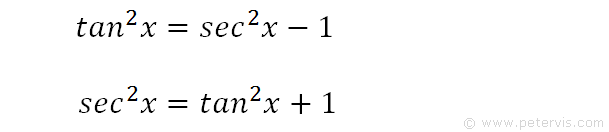


Integrate Sec 2x Method 1


Solved Prove The Following Trig Identity Sec 2 X 2secx Cosx Cos 2 X Tan 2 X Sin 2 X Course Hero
Expert Answer Previous question Next questionIntegration of tan^2x sec^2x/ 1tan^6x dx Ask questions, doubts, problems and we will help youFree math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutor


Chapter 5


Tan2x ただの悪魔の画像
Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutorMay 07, 15 · Well, if we divide (cos(x))2 on both sides;Hi Simplifying the following (sec^2x csc^2x)(tan^2x cot^2x) tan^2x = sec^2x 1 cot^2x = csc^2x 1 (sec^2x csc^2x)(sec^2x 1 csc^2x 1)= 2 Answer by MathLover1() (Show Source) You can put this solution on



Integral Of Sec 2x Tan X



Slides Show
Prove that tan^2x sec^2x=1 Answers 3 Get Answers answered Guest answer b stepbystep explanation x2 = 16 x can not be a negative number because 16 is positiveSep 19, 14 · Evaluate $\displaystyle \int \tan^2x\sec^2x\,dx$ I tried several methods First method was I changed $\tan^2x = \sec^2x1$, and then substitute $\sec x$ to $t$, butTan(x y) = (tan x tan y) / (1 tan x tan y) sin(2x) = 2 sin x cos x cos(2x) = cos ^2 (x) sin ^2 (x) = 2 cos ^2 (x) 1 = 1 2 sin ^2 (x) tan(2x) = 2 tan(x) / (1
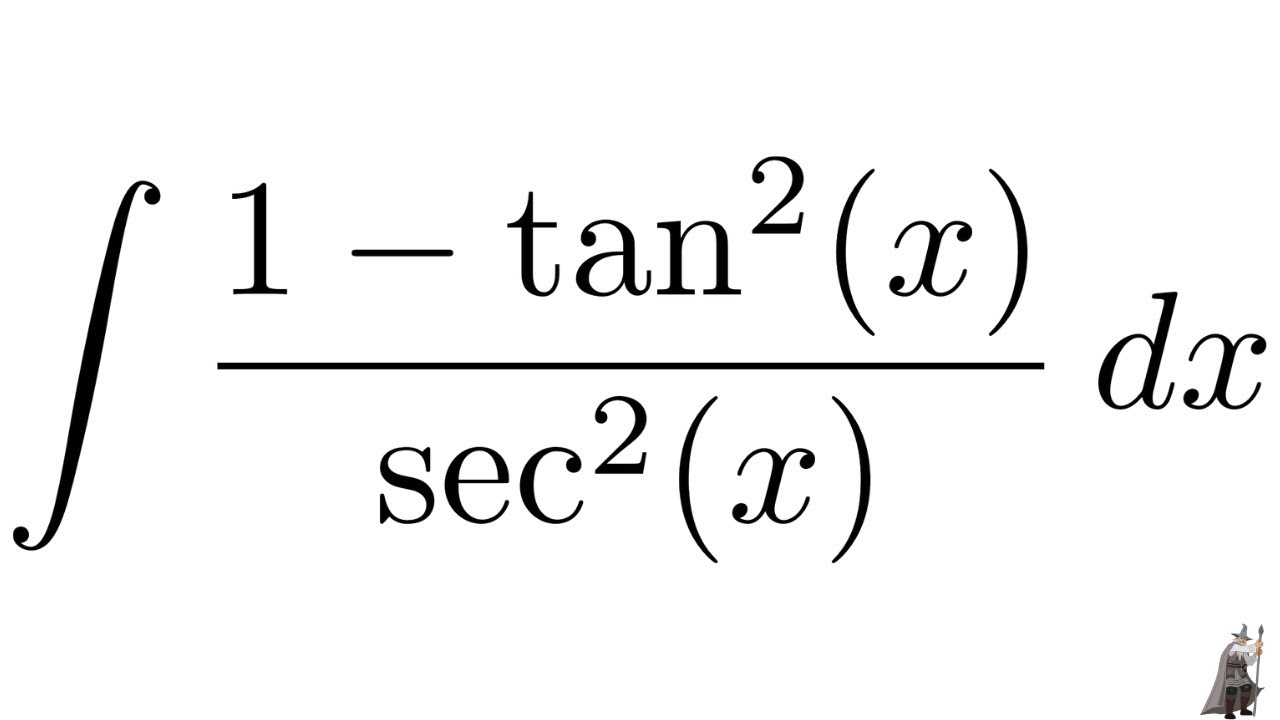


Integral 1 Tan 2 X Sec 2 X Youtube


Solution Verify The Identity By Showing That The Left Equals Right Sec 2x 1 Tan 2 Sec2x Do I Use 1 Cos 2x 1 Tan 2x Or Do I Use 1 Tan 2x 1 Tan 2x Either Way I Do Not Know Where To Go Fro
Jan 13, 13 · A few hints 1 sec x = 1/(cos x) 2 (sin x)/(cos x) = tan x That should give you a good start



3 Sec 2x1 Cos 2x Tan 2x Tan X Esus Is Always The Anse Ja Irl Meme On Me Me



Sec 1 1 Tan 2x 1 Tan 2 X



Int Tan 2xsec 2x 1 Tan 6x Dx



Question Video Differentiating Functions Involving Trigonometric Ratios Using Pythagorean Identities Nagwa



Ex 3 4 8 Find General Solution Of Sec 2 2x 1 Tan 2x Teachoo


Solution Tan 2x Secx 1 1 Cosx Cosx Please And Thank You



Omtex Classes Iv Sec6x Tan6x 1 3 Sec2x Tan2x



Mathematics Question Of The Day With Solution Facebook



Tan2x Tanx Tanx Sec2x Maths Trigonometric Functions Meritnation Com


Tinkutara Equation Editor Math Forum Question


Solved Consider The Possible Identity Tan 2x Cos 2x 1 Cos 2x Sec 2x A State Any Non Permissible Values B Attempt To Verify Possible Identity Course Hero



Ex 3 4 8 Find General Solution Of Sec 2 2x 1 Tan 2x Teachoo



Answered 3 1 Tanx Tan 2x Sec 2x S Bartleby
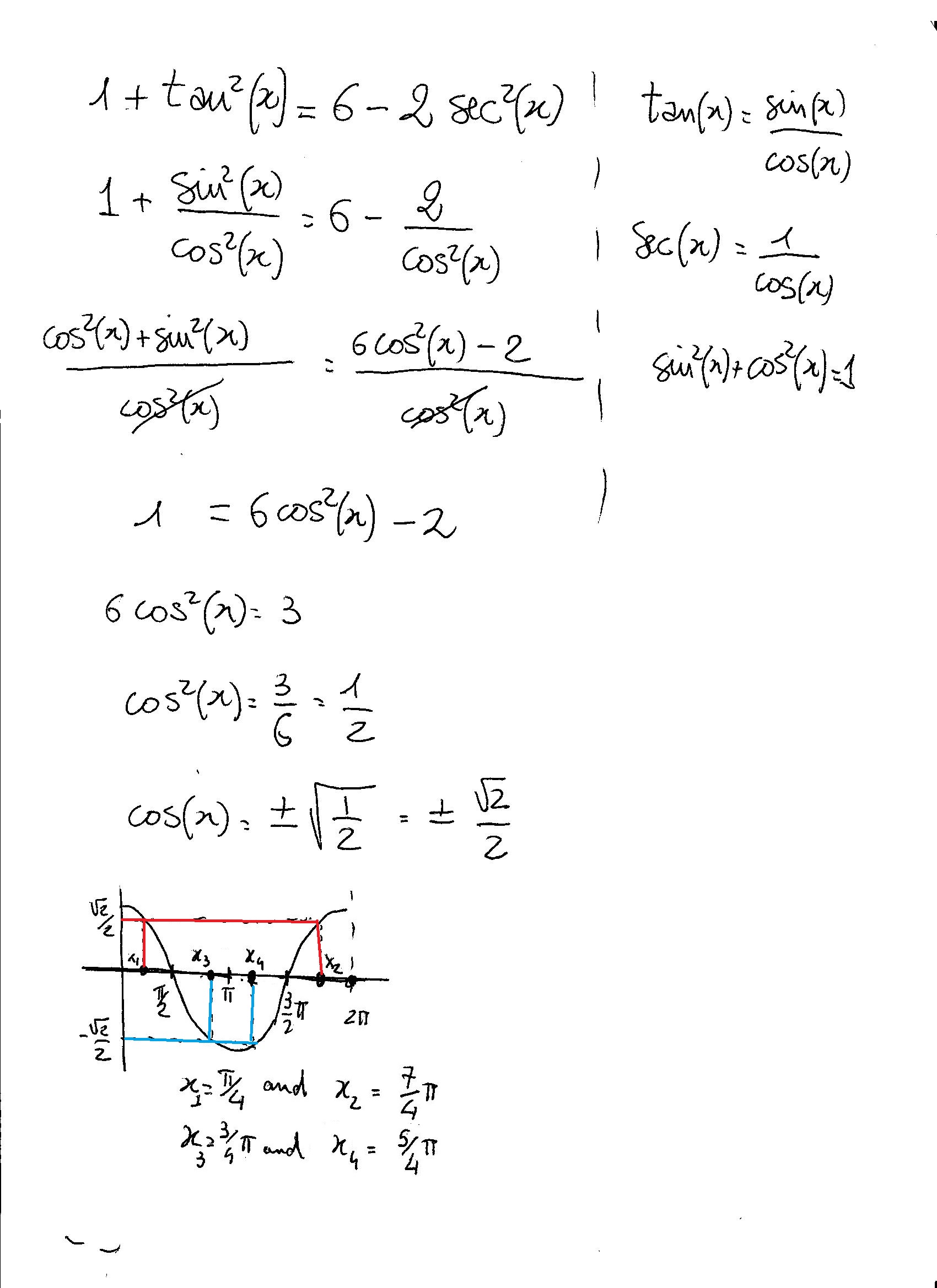


How Do You Solve 1 Tan 2x 6 2sec 2x Socratic



Egua8pk Nue Zm



F 2tanx 1 Tan 2x Cos2x 1 Sec 2x 2tanx 2



Finding The Derivative Of Sec 2 X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Derivative Of Tan 2x Sec 2x


Answered Stan 2x Cos 2x Dx Tan 2x 2 V Sec 2x Bartleby
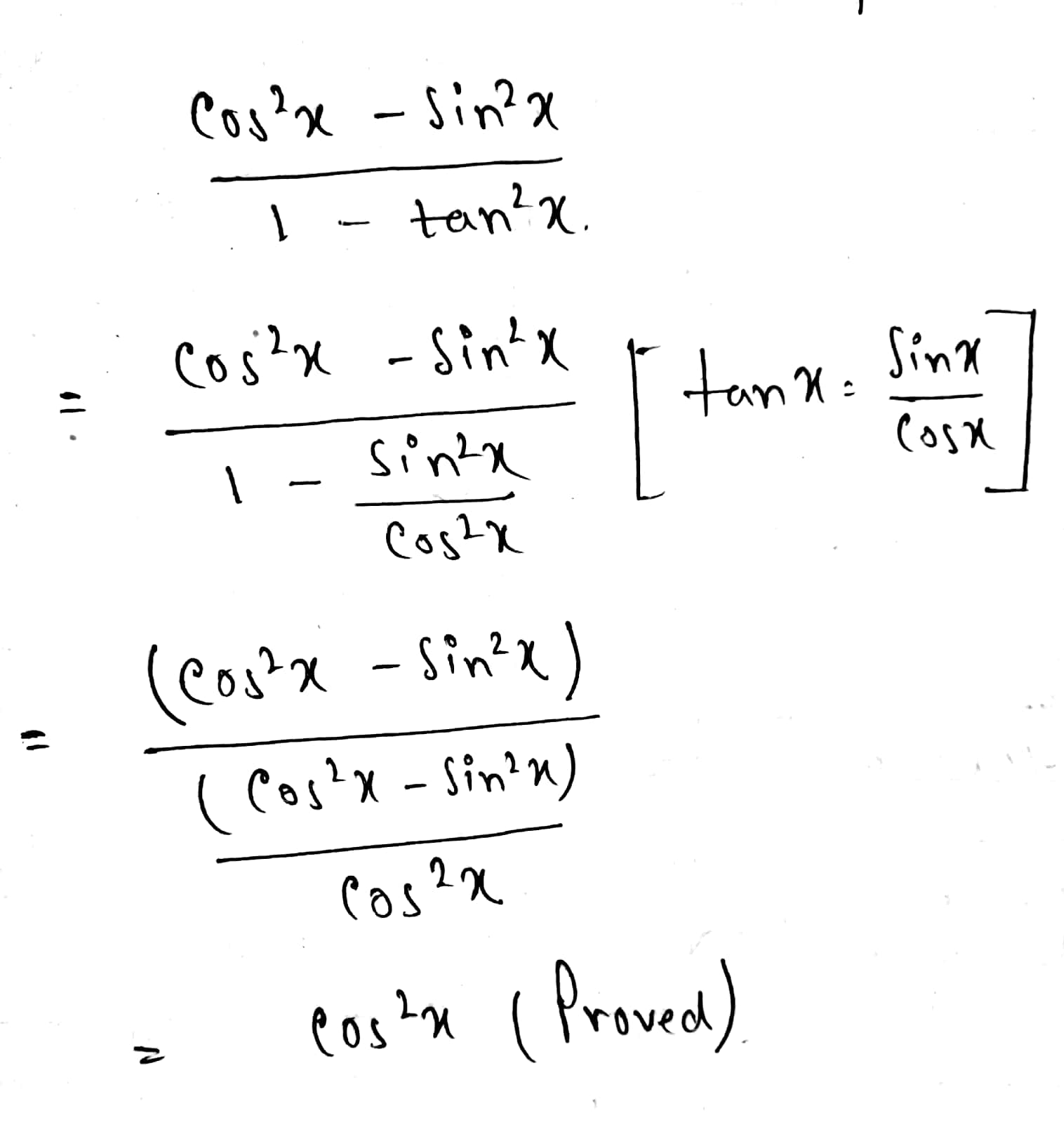


How Does One Verify Cos 2x Sin 2x 1 Tan 2x Cos 2x Socratic



How Do You Prove Tan 2x Secx 1 1 Secx Socratic
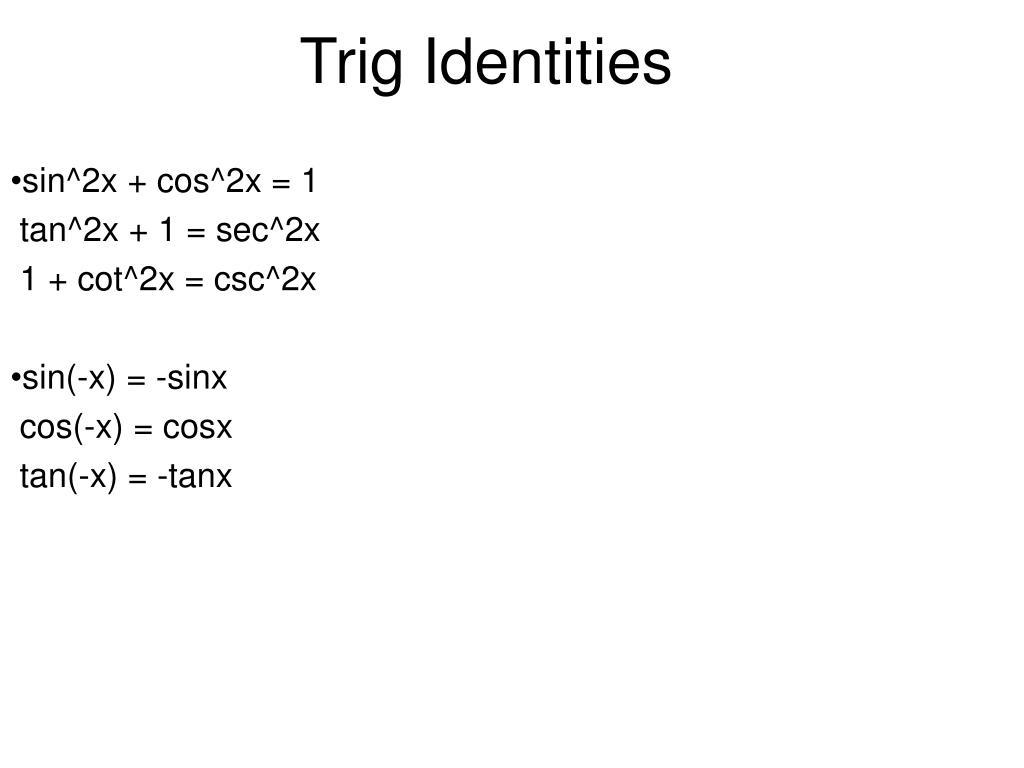


Ppt Analytic Trig Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
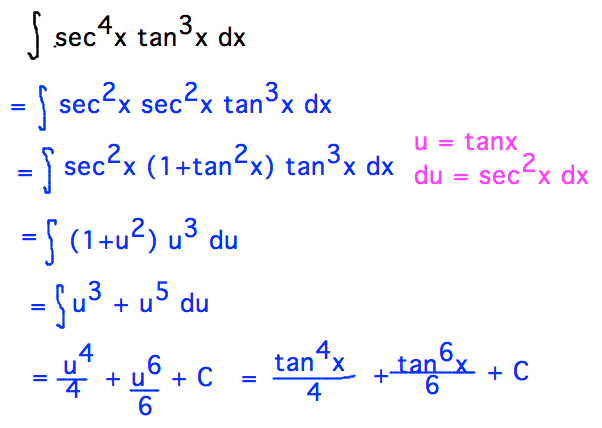


Geneseo Math 222 01 Trigonometric Integration



Answered Find The Indefinite Integral Sec 2x Bartleby



How Many Can You Derive From First Principles Ppt Download


Trigonometric Substitution



Slides Show


Sec 2x Tan 2x 爱恋壁纸网



Integral Of Tan 2x Cot 2x 2 Calculus 1 Trig Integrals Calculus Mathematics Email Subject Lines



Find The General Solution For Each Of The Following Equations Sec2 2x 1 Tan 2x Mathematics Shaalaa Com



How Do You Integrate 1 Tan2x Sec2x Dx Socratic



1 Cosx 1 Cosx Tan 2x Secx 1 2prove Brainly In
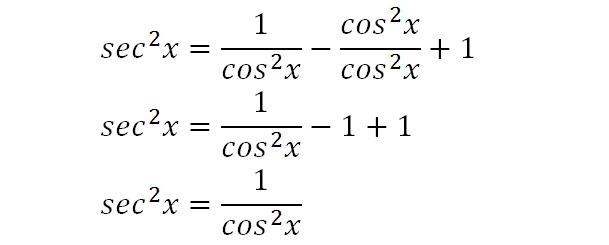


Integrate Sec 2x Method 2



Byjok H9 9y3gm


What Is The Integral Of Tanx Sec 2x E Tanx Quora


Solutions To Odd Number Exercises Lo Y Sec 2 Period



Get Answer 1 Tan2x Sec2x Dx Sin2x 2 C Tan 2 X 2 C 2sin X Cos X Transtutors



Solved Verify The Identity 4 2 Tan X Secx2tan X 1 Whic Chegg Com


Tan 2x Sec 2x 1 Also Tan Sec 1 Or Am I Missing Something Physics Forums



25 Best Memes About X Tan X Tan Memes
.JPG)


Every Day I M Calculatin I D3 Unit Q Pythagorean Identities
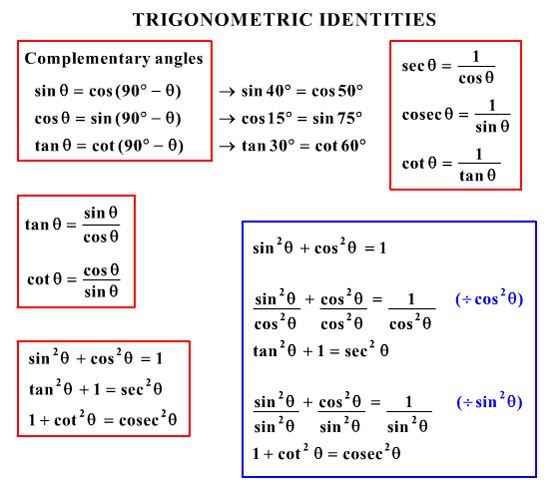


What Would Be Steps In Proving That Tan2x Secx 1 1 Sec X Socratic



9 1 Identities And Proofs Ppt Download



Formulas And Identities Flashcards Quizlet
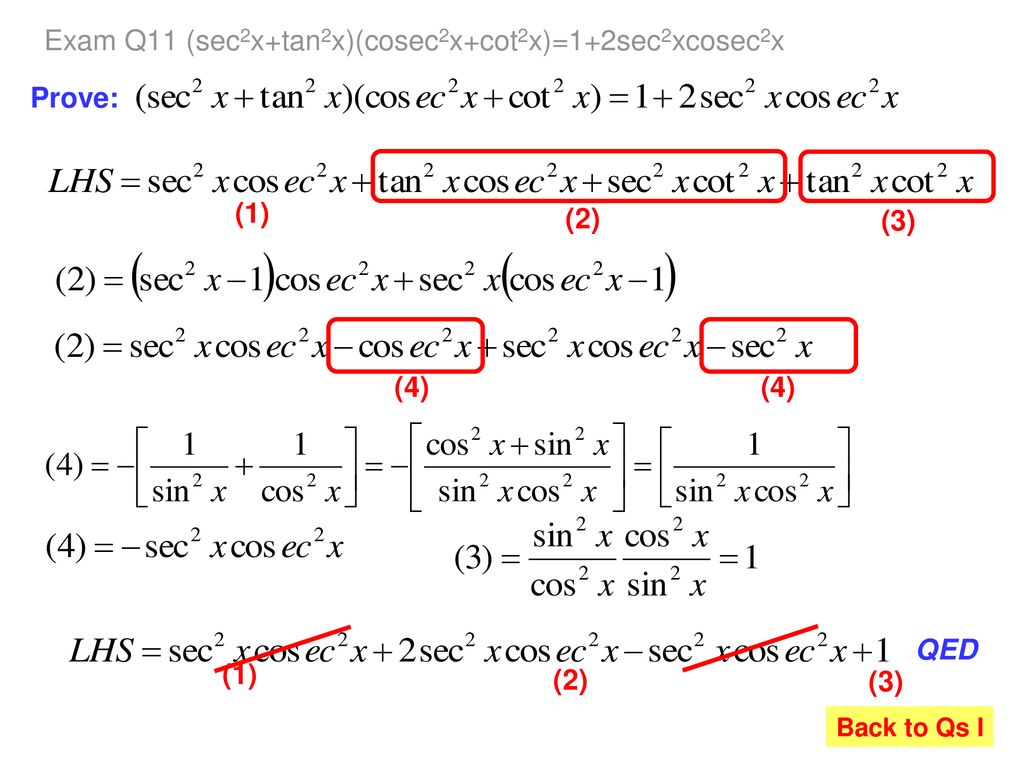


How Many Can You Derive From First Principles Ppt Download



Tentukan Hp 2 Tan 2x Sec X 1 0 Untuk 0 Lt X Lt 2 Brainly Co Id



Solved If 2 Tan2x Secx 1 Which Of The Following Are Tru Chegg Com



Solve Tan 2 X 1 0 Yahoo Answers Noha Matthieu Lire Un Livre



Sec 2x 1 Gallery Cute766



Finding The Derivative Of Sec 2 X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Find The Derivative Of The Given Function Y Tan 2x 1 Cot 2x I Tried Converting The Original Function In Terms Of Sin And Cos But It Was Still Too Complicated To Be Called Simplified



If Tan 2 X Sec X A 0 Has Atleast One Solution Then Complete Set Of V Askiitians
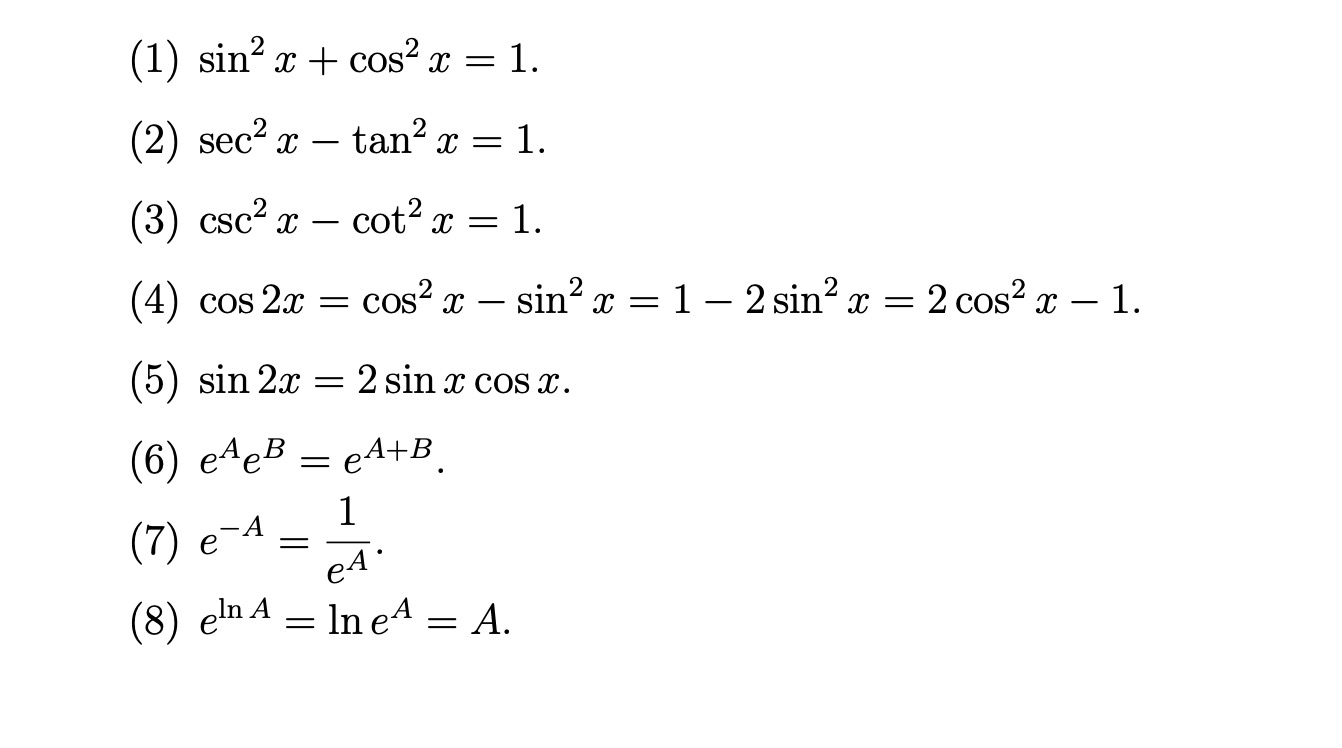


Here Is A List Of Identities Involving Trigonometr Chegg Com


If Y Tan 1 2x 1 X 2 Sec 1 1 X 2 1 X 2 X 0 Prove That Dy Dx 4 1 X 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Dopl3r Com Memes 3 Sec2x 1 Cos 2 X Tan 2x Tan X Esus The An Is Always 5



How Do You Simplify Sec 4x Tan 4x Sec 2x Tan 2x Socratic


8 Solve The Equation Sec C22x See How To Solve It At Qanda
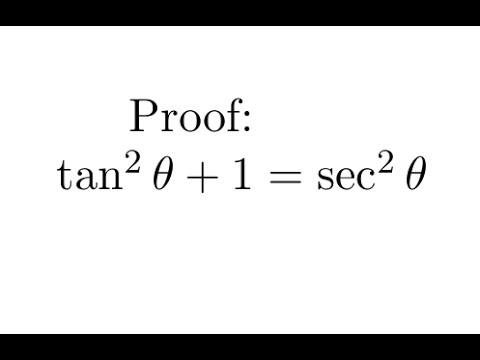


Proof Tan 2 1 Sec 2 Youtube
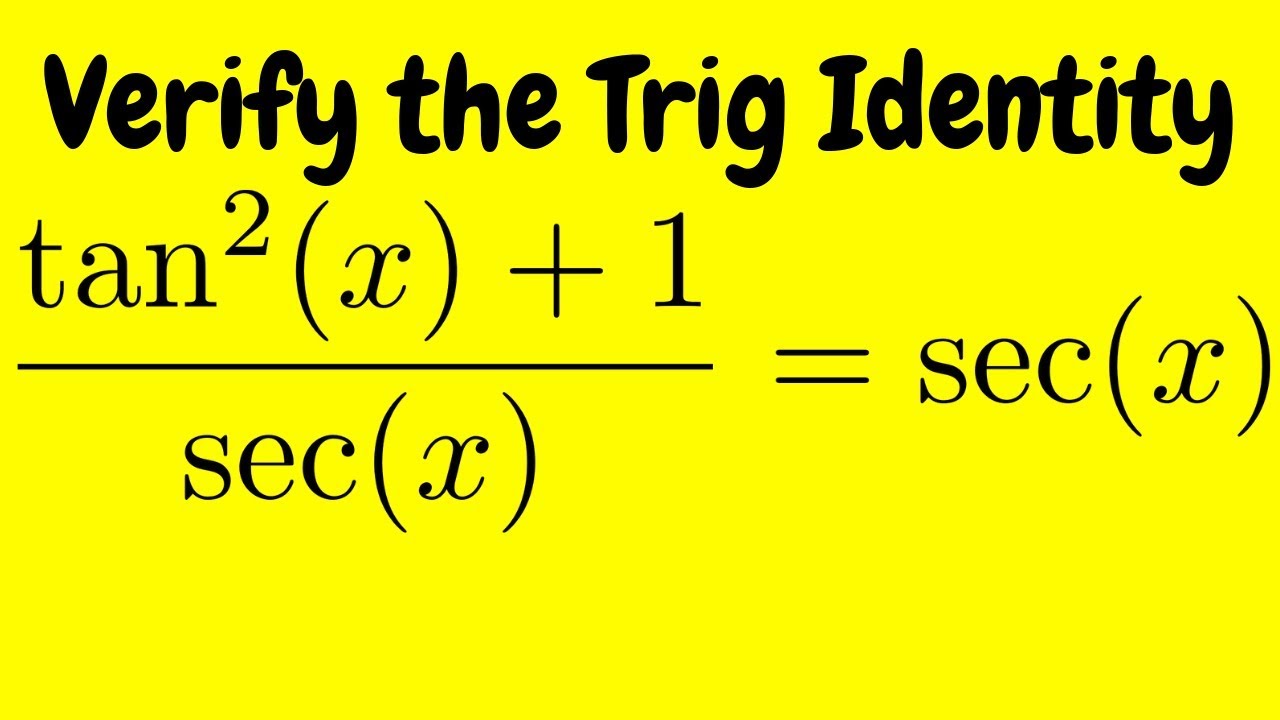


Verifying A Trigonometric Identity Tan 2 X 1 Sec X Sec X Youtube


How To Prove Csc 2x 1 Tan 2x 1 Is Equivalent To Cosec 2x Quora


Prove That Sec 4x Sec 2x Tan 2 X Tan 4x
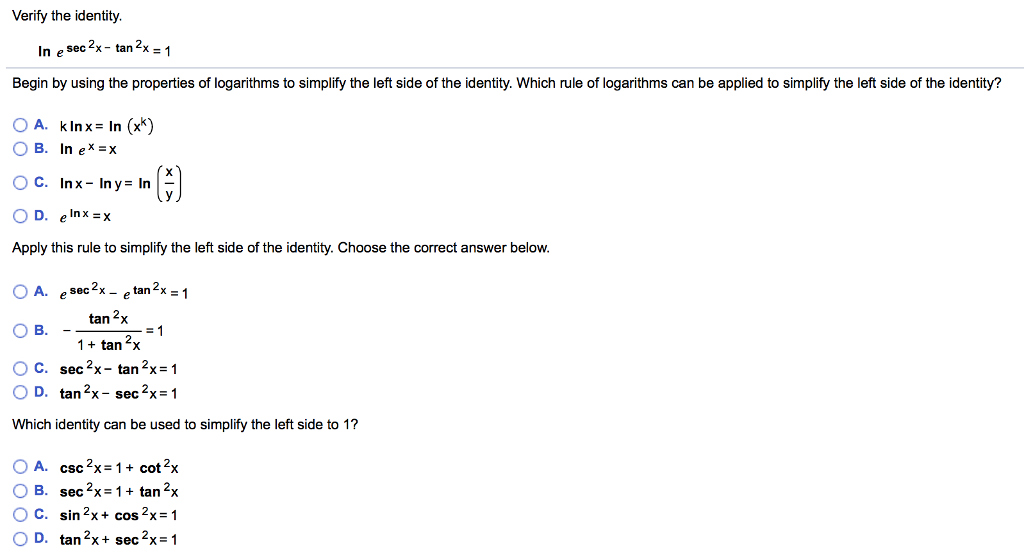


Solved Verify The Identity In Esec 2x Tan 2x 1 Begin By Chegg Com



Ex 3 4 8 Find General Solution Of Sec 2 2x 1 Tan 2x Teachoo



Cy91m8fq6sistm



The Derivative Of Sec2x Derivativeit



Int Tan 2x Secx 1 Dx Youtube



Is There Any Other Way To Establish This Trig Identity Frac Sec X 1 Tan X Frac Sin X 1 Cos X Mathematics Stack Exchange
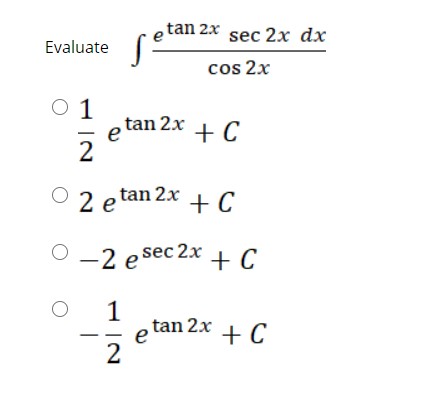


Answered Tan 2x Sec 2x Dx Evaluate Cos 2x O 1 Bartleby


Integrate Sec 2x Method 2



7 2 47 Integral Of 1 Tan2x Sec2x Cute766


What Is The Differentiation Of Sec Inverse Tan 2x Quora



Sec 2x1 Cos2 X Tan 2x Tantx 3 Esus Is Always The Ans イais 1 0 If You Are A Student Follow Tumblr Meme On Me Me



Tan2x ただの悪魔の画像



Sec22x 1 Tan 2x Find The General Solution Maths Trigonometric Functions Meritnation Com
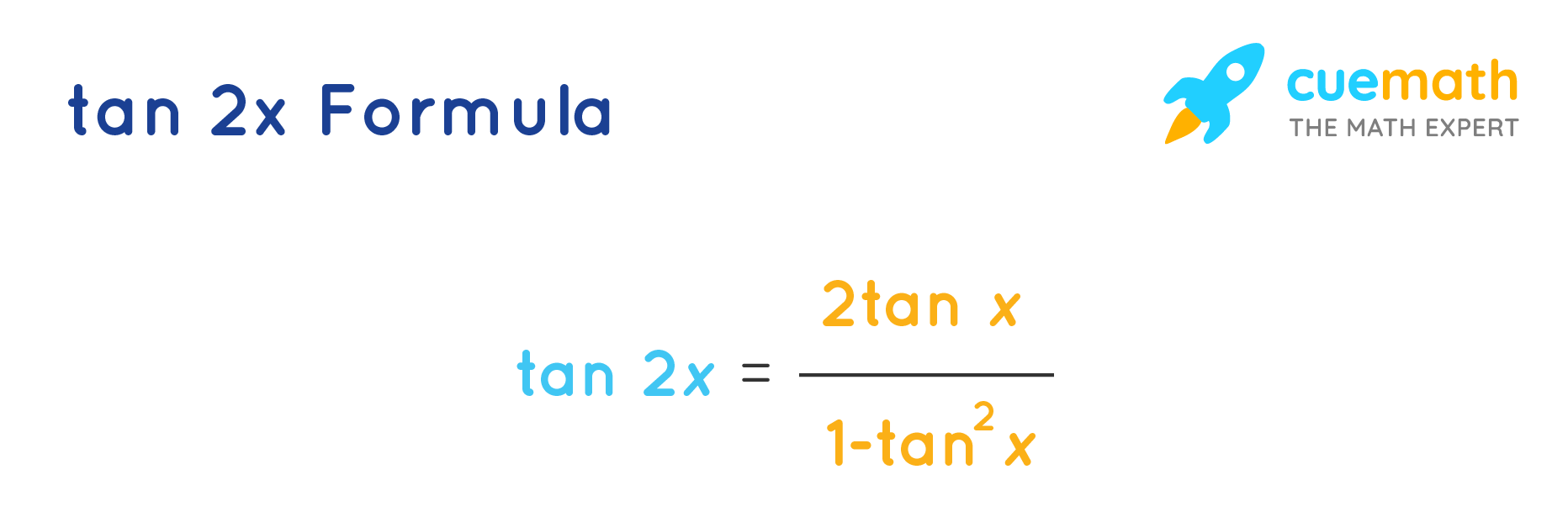


Tan 2x Formula Learn Formula For Calculating The Double Angle Tan 2x



How To Show That Math Tan 2 X Sec 2 X 1 Math Quora



Solve Tan 2 X 1 0 Yahoo Answers Noha Matthieu Lire Un Livre


